In industries where ropes are exposed to high temperatures—such as firefighting, rescue operations, foundries, welding sites, or heavy industry—the right choice of rope can mean the difference between safety and failure. A heat resistant rope is specifically engineered to maintain its integrity under extreme thermal conditions, ensuring both reliability and protection.
A heat resistant rope is a specialized cordage designed to withstand high temperatures, making it essential in various industrial and safety applications. Manufactured from materials like fiberglass, aramid fibers (e.g., Kevlar, Nomex), and ceramic fibers, these ropes offer superior performance in extreme conditions.
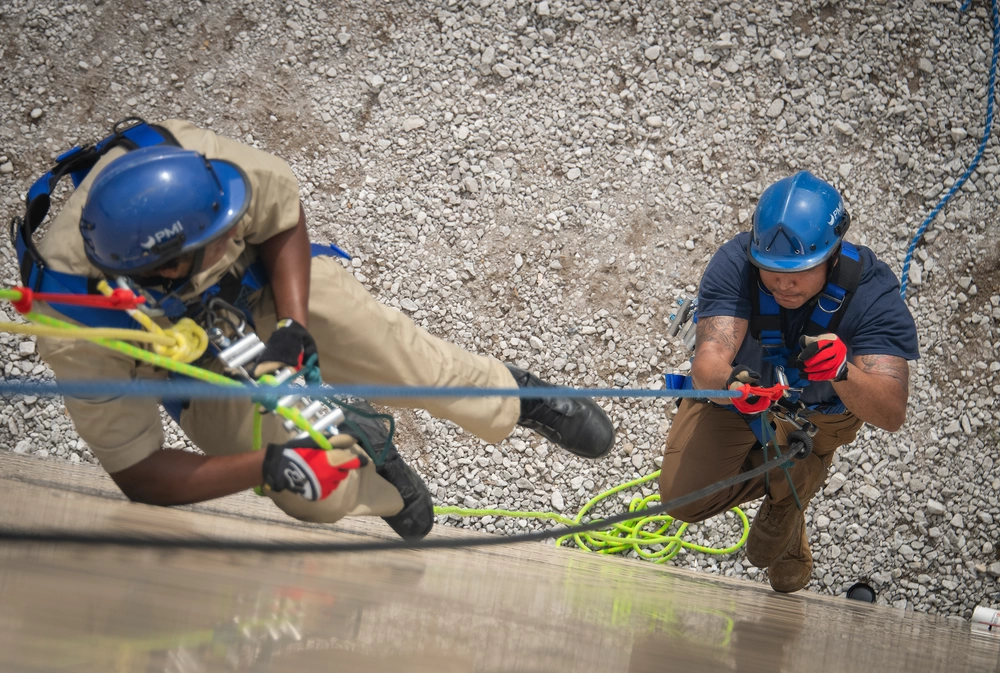

Conventional ropes (e.g., standard polyester or nylon) begin to lose strength when exposed to temperatures above 150–200 °C. In contrast, ropes
manufactured from aramid fibers (like Kevlar® or Technora®) or basalt/glass composites can withstand continuous exposure to 400–500 °C and
short-term peaks exceeding 800 °C.
Benefit: Workers and rescue teams can operate safely in environments where ordinary ropes would melt, shrink, or fail.
Heat resistant ropes are designed not only to resist melting but also to retain tensile strength under thermal stress. For example:
Kevlar® maintains ~50% of its room-temperature strength even at 300 °C.
Technora® demonstrates exceptional resistance to creep and degradation when heated.
This means the rope remains reliable for load-bearing, anchoring, and safety-critical tasks, even in high-temperature environments.
In addition to thermal resistance, many heat resistant ropes also offer:
Excellent abrasion resistance (important in firefighting and rescue where ropes run over rough edges).
Chemical resistance to fuels, solvents, and acids.
UV resistance, prolonging service life in outdoor use.
Low elongation, which minimizes sudden slack and improves control during rescue or lifting operations.
Firefighting and Rescue: Assisting evacuation or line deployment in high-heat environments.
Industrial Maintenance: Working near furnaces, kilns, or welding operations.
Military and Marine: High-performance cordage where both flame and abrasion resistance are crucial.
Rigging in Hot Work Areas: Securing loads exposed to sparks or radiant heat.
A heat resistant rope is not just a stronger rope—it is a safety solution tailored to environments where ordinary fibers fail. By withstanding extreme temperatures, maintaining structural integrity, and resisting harsh external factors, these ropes provide critical protection for professionals working in high-risk industries.